Network
This section shows how to configure network settings and tools for network connectivity in AhsayUBS through the AhsayUBS WebAdmin.
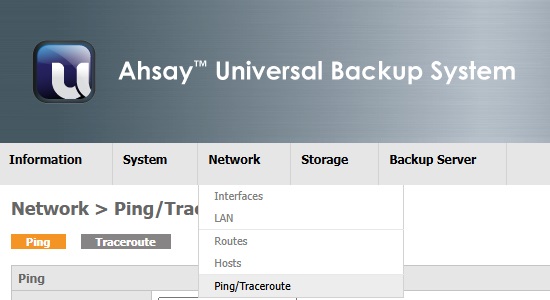
When the mouse is pointed over the word "Network" in the menu bar, the following menu will be displayed:
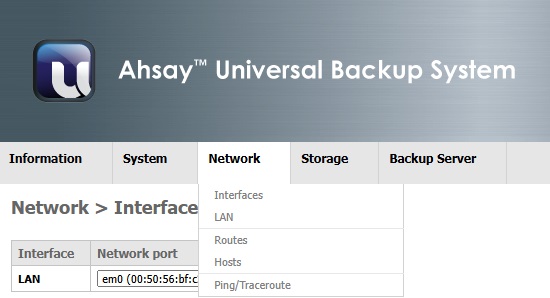
- Interfaces (Assign the physical device with a configuration setting)
- LAN/OPT1/OPT2 (Configuration for interface LAN/OPT1/OPT2)
- Routes (Current routing information)
- Hosts (User defined Host - IP Address mapping)
- Ping/Traceroute (Network tools)
Interfaces
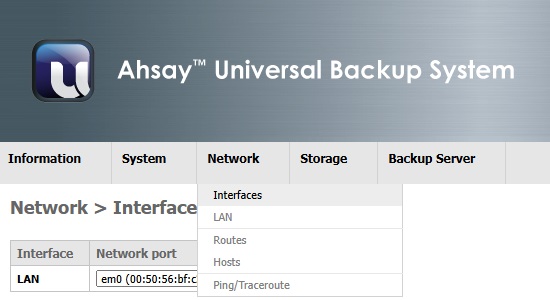
This page shows a summary of physical network devices in AhsayUBS. The first column shows the interface name (e.g. LAN). The second column shows the network port’s name and its physical address.
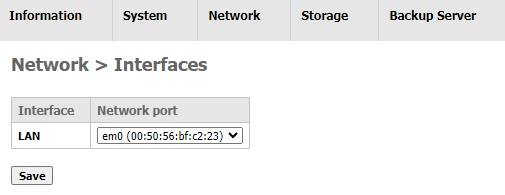
By default, there should be at least one network device which will be assigned as LAN in the system.
-If there are other network interfaces available in the system, an Add button will be shown next to the table for addition of other network interfaces.
You can assign different network device to the interface name from the dropdown list at the second column. After selecting the interface, click the Save button to save your settings.
Once you have added an OPT1 network interface, a new configuration page Network > Optional 1 (OPT1) will be added to the system after reboot.
The Network > LAN denotes the network device configuration for the network device which has been assigned at the Network > Interface page. Additional network interfaces OPT1 can be configured at the page Network > OPT1 which is similar to the LAN interface.
In addition, a network interface can be deleted by clicking the Delete icon corresponding to the network interface that you want to delete. After rebooting AhsayUBS, the network interface will be deleted successfully.
LAN/OPT1/OPT2
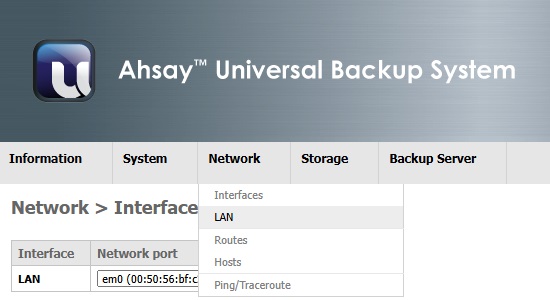
This page helps to set the configuration of the network interface labeled LAN in AhsayUBS.
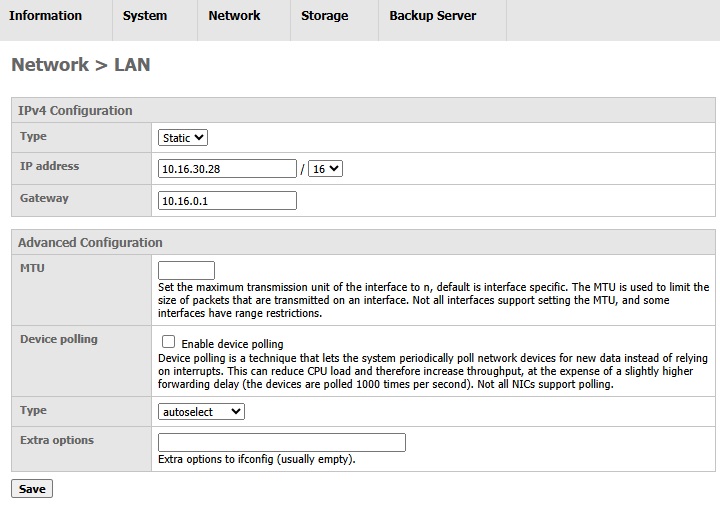
IPv4 Configuration
The fields for this section are listed below:
- Type: Select "DHCP" to obtain the IP address automatically. Select "Static" for entering the IP address manually.
- IP Address: This will be enabled only in STATIC mode. You need to enter the IP address for AhsayUBS. Please make sure that the IP address entered can be reached from your computer. The drop down list after the "/" is the subnet mask. The value here represents the number of bits of the subnet mask address e.g. if the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0 (i.e. in binary form: 11111111.11111111.111111111.000000000), the subnet number is 24 bit.
- Gateway: This will be enabled only in STATIC mode. The default gateway must be entered correctly.
Advanced Configuration
The fields for this section are listed below:
- MTU: Set the maximum transmission unit of the interface to n, the default setting is leave to n, default is interface specific (i.e. blank). The MTU is used to limit the size of packets that are transmitted on an interface. Not all interfaces support setting the MTU, and some interfaces have range restrictions.
- Device polling: Device polling is a technique that lets the system to periodically poll network devices for new data instead of relying on interrupts. This can reduce CPU load and therefore increase throughput, at the expense of a slightly higher forwarding delay (the devices are polled 1000 times per second). Not all NICs support polling.
- Type: Select the speed of network from the drop-down list.
- Extra option: You can enter extra options for the FreeBSD command ifconfig here. For more information on this command, please refer to the FreeBSD documentation.
After the configuration is updated, the page is refreshed. If a reboot message is shown, please click the link reboot in the message to reboot AhsayUBS for the changes to take effect.
Routes
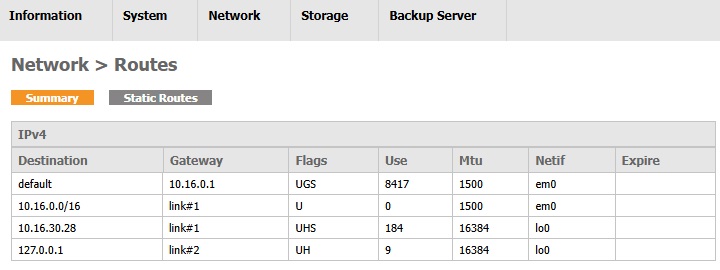
Summary
This page shows the routing table of your AhsayUBS which is used to trace the network routing to a target network destination.
Static Routes
This page allows you to customize the static route. If there are several network interfaces in AhsayUBS, additional routes can be added to allow directing network traffic to other networks.
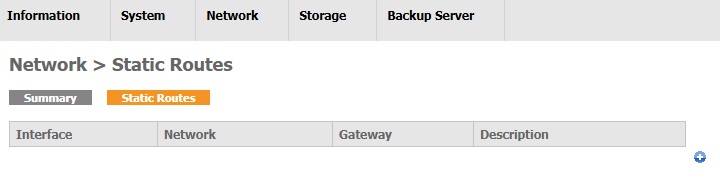
If you want to add a static route, click the Add Route icon to continue.
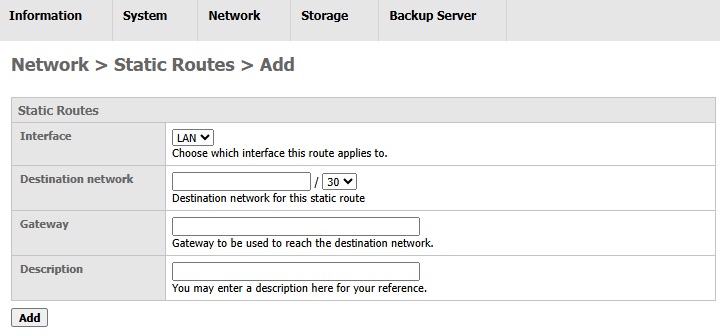
The static routes table will then appear on the browser. Here are the rows that you can configure:
- Interface: Select the interface that will be used for the static route.
- Destination network: The network where the traffic should be directed to via the "Gateway".
- Gateway: The IP address of the gateway which has been connected to the destination network.
- Description (Optional): Enter some comment related to this static route entry.
Click the Add button after completing the table, the message "The configuration has been changed" will appear when the entry is added successfully.
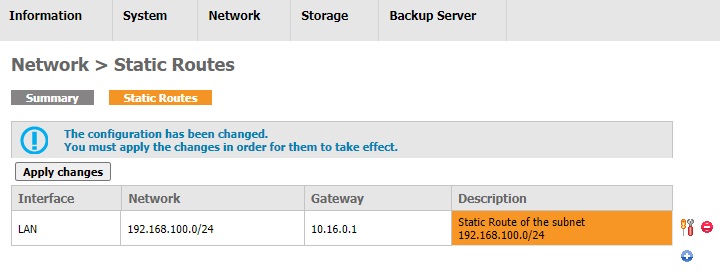
Click Apply changes for the changes to take effect.
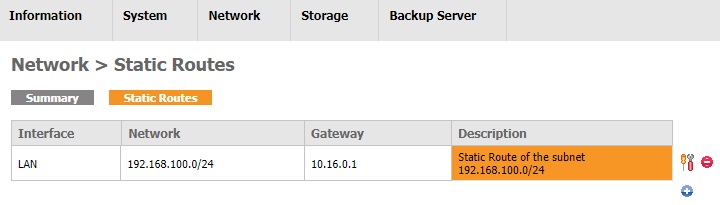
Now you can click the Edit Route icon to configure the entry or click the Delete Route icon to remove the entry.
- Edit: Edit the entry and click the Save > Apply changes button to save the changes.
- Delete: After clicking this icon, a pop-up dialog will appear to confirm the changes. Click the OK button to confirm deletion or click the Cancel button to abort. After the dialog is closed, the message "The configuration has been changed" will be displayed. You need to click the Apply changes button to delete the entry.
Hosts
This page is for the customization of hosts settings.
Summary
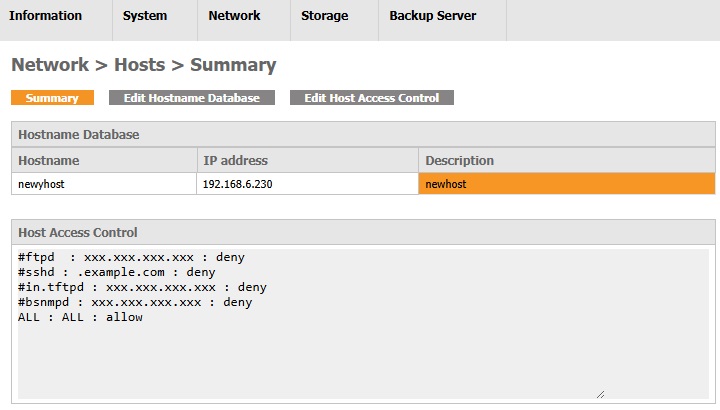
It contains a summary of the entire host settings inside AhsayUBS.
The Hostname Database table contains the mapping of the hostname and IP address inside AhsayUBS.
Here are the fields required for each of the hostname database entry:
- Hostname: The hostname you want to map with IP address in the "IP address" field.
- IP Address: The IP address you want to map with the hostname in the "Hostname" field.
- Description (Optional): Enter some description of the mapping for your reference.
You may edit the hostname database settings in the page Network > Hosts > Edit > Hostname Database.
The Host Access Control table contains the settings of the access control of the specific daemon.
The basic configuration usually takes the form of daemon:address action, where daemon name of the service started. The address can be a valid hostname, and IP address enclosed in brackets. The action field can be either allow or deny to grant or deny access appropriately. Keep in mind that configuration works off a first rule match semantic, meaning that the configuration file is scanned in ascending order for a matching rule. When a matching result is found, the rule will be applied. Then, the search process will halt. To get detailed information about TCP wrappers, please refer to the FreeBSD documentation.
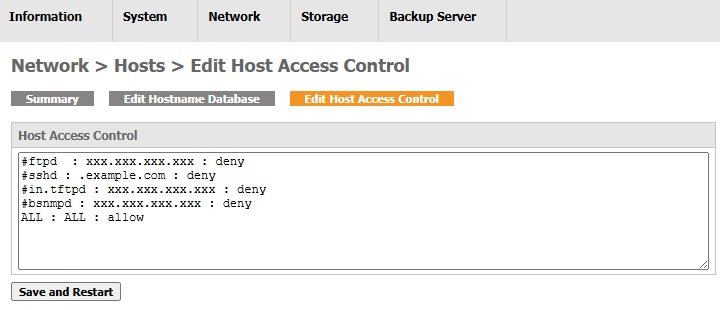
The default settings of the Host Access Control are:
#ftpd : xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx : deny
#sshd : .example.com : deny
#in.tftpd : xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx : deny
#bsnmpd : xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx : deny
ALL : ALL : allow
You may edit the host access control settings in the page Network > Hosts > Edit Host Access Control.
Edit Hostname Database
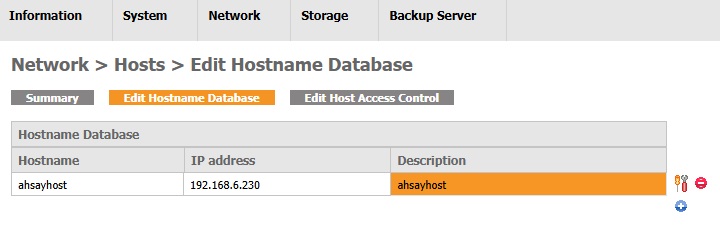
Add a hostname database entry
- (Entry Exist) Click the Add Hostname icon.
Fill in the required fields.
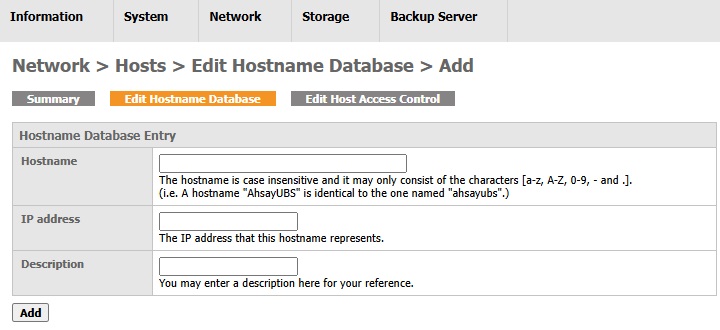
- Click the Add button.
A new entry is added successfully to the hostname database.
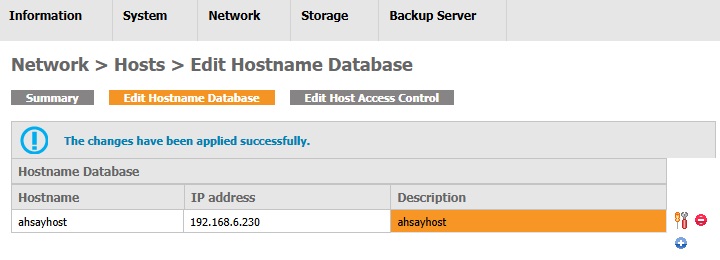
Edit a hostname database entry
- Look for the entry to be edited.
- Click the Edit Hostname icon.
Edit the fields.
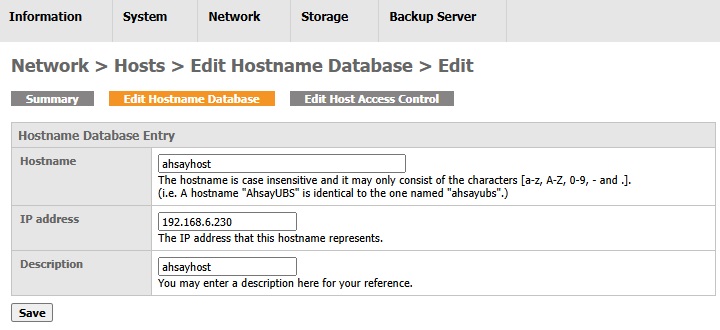
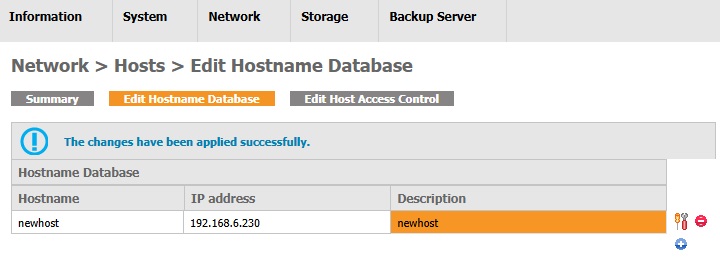
- Click the Save button.
The entry is edited sucessfully.
Delete a hostname database entry
- Look for the entry to be deleted.
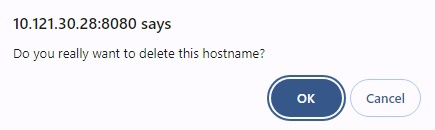
- Click the Delete Hostname icon.
Click OK to confirm deletion.
- The entry is deleted sucessfully.
Edit Host Access Control
Edit the entries in the Host Access Control text area and click the Save and Restart button to update and restart the server. The new settings will take effect after restarting the services.
Ping/Traceroute
This page contains the network tools: ping and traceroute.
Ping
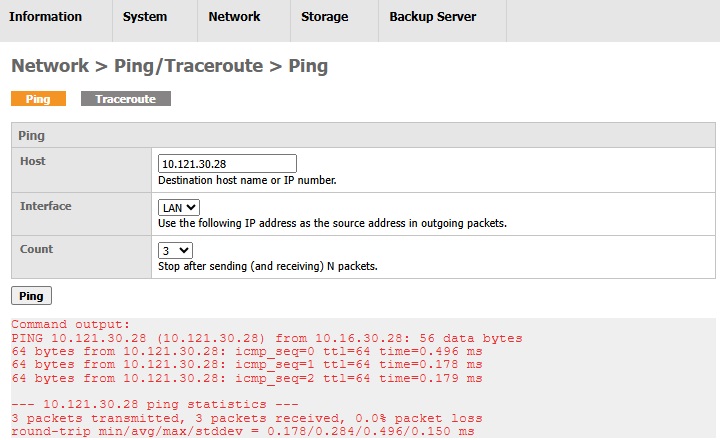
A command (i.e. "ping") in standard UNIX machines. It tests whether your AhsayUBS network interface can reach the destination hosts specified. After you have entered the required information in the text box, click the Ping button to ping the destination host. The results will be shown below whether the destination can be reached by AhsayUBS or not.
Below is an example where AhsayUBS can reach the destination successfully.
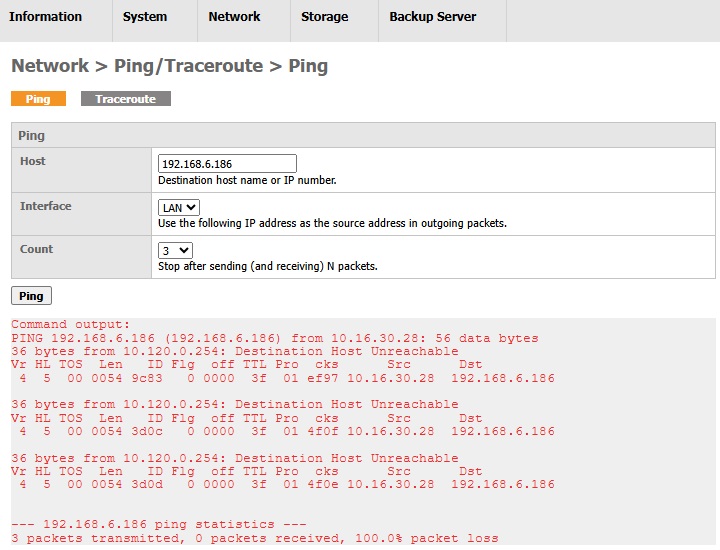
Below is an example where AhsayUBS failed to reach the destination "192.168.6.186".
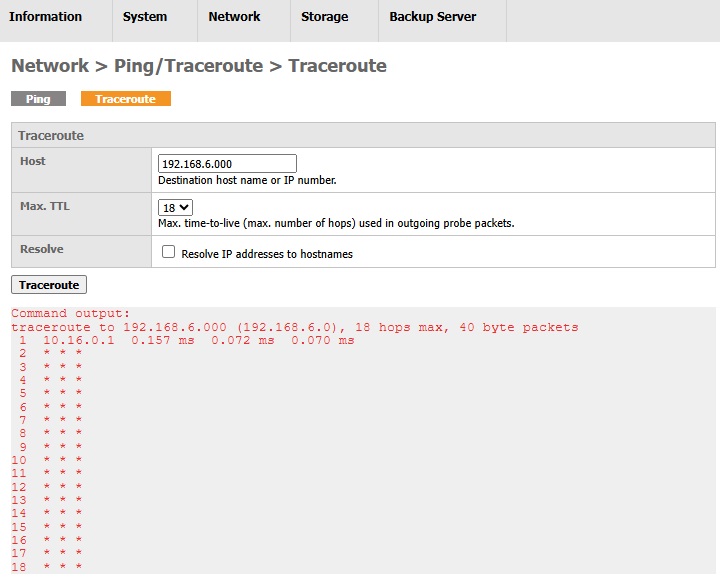
Traceroute
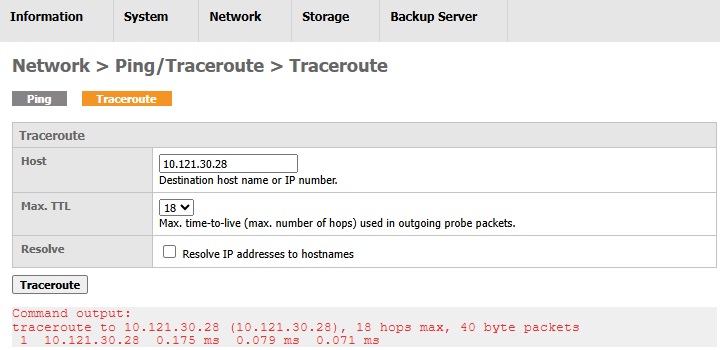
Traceroute is another tool for testing your AhsayUBS network connection to a destination host you entered in the table below. It also shows the path that packets travel from AsayUBS to the destination host.
Below is an example where AhsayUBS can reach the destination successfully.
Below is an example where AhsayUBS failed to reach the destination.

 How-To
How-To